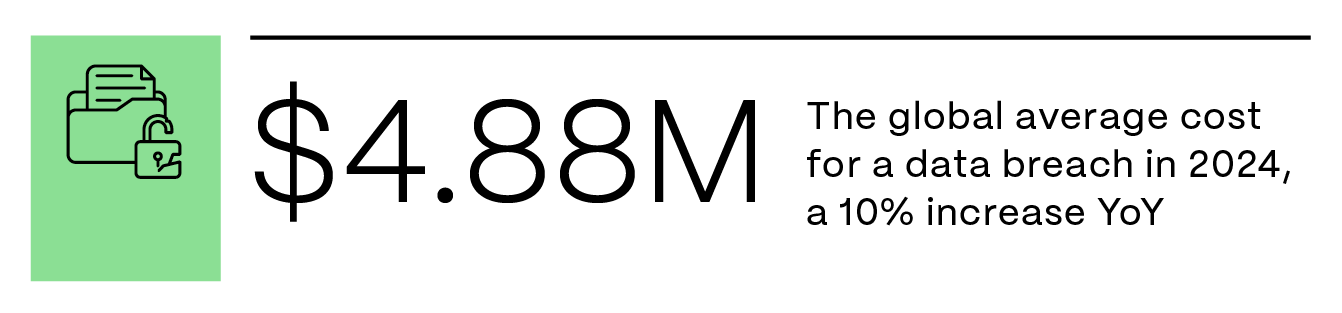
Blog
The future of cybersecurity: key trends for 2025 and beyond

The future of cybersecurity: key trends for 2025 and beyond
The rise of cloud services and IoT (Internet of Things) devices has dramatically transformed how businesses and consumers interact with technology. This innovation has sparked the growth of new ventures and global collaboration. However, it has also widened the attack surface, leaving organizations more vulnerable than ever to cyber threats.
As we enter Cybersecurity Awareness Month, understanding the evolving landscape of cyber risks and how to safeguard your assets has never been more critical. This article will explore cybersecurity trends for 2025 and beyond, offering insights that can help businesses of all sizes navigate the digital age securely.
Introduction to the future of cybersecurity
Heading into 2025, the global average cost of a data breach has reached an all-time high of$4.88M — a 10% rise over 2023. With advancing technology and increasingly sophisticated attacks, businesses must remain vigilant and ready to adapt. By understanding and addressing the cybersecurity trends of 2025, organizations can proactively safeguard data, protect systems, and maintain business continuity.
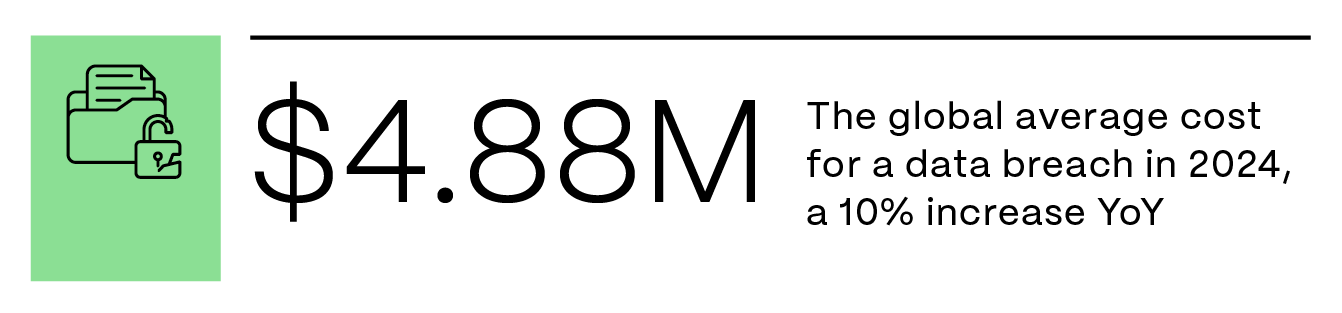
5 key cybersecurity trends for 2025
Ever wondered, “what are the top three trends in the cybersecurity industry?” This section explores leading trends for 2025, from AI-powered defenses to a heightened focus on supply chain security.
1. Harnessing AI for cybersecurity
Recent research predicts that by 2025, the number of U.S. companies investing $10M or more in AI (artificial intelligence) will nearly double. Beyond enhancing productivity, AI will play a pivotal role in automating threat detection, analyzing large datasets, and predicting vulnerabilities in real time. By recognizing patterns and anomalies that human analysts might miss, AI significantly reduces response times.
However, bad actors will also harness AI to create more complex threats, such as AI-generated malware and advanced phishing campaigns. With defenders and attackers both leveraging the power of AI, this makes the cybersecurity arms race even more dynamic.
2. Adopting zero trust architecture
Based on the principle of "never trust, always verify,” thezero trust security model will dominate protection strategies in 2025. Zero trust frameworks operate on the idea that every user, device, and connection – inside or outside the network – must be continuously authenticated and authorized. With the rise of hybrid work and distributed networks, zero trust will help mitigate insider threats, reduce attack surfaces, and providegranular access control across all endpoints.
3. Safeguarding supply chains
Supply chain protection will become a priority as businesses acknowledge the exposures posed by third-party vendors and partners. Arecent survey showed that security incidents linked to third parties have nearly doubled year over year. Plus, high-profile breaches like the SolarWinds hack have put a spotlight on the risks within supply chains.
In response, organizations must implement stricter vetting, monitoring, and security protocols for external vendors. Enhanced collaboration and information sharing across industries will be key to detecting and mitigating supply chain risks before they spread through interconnected systems.
4. Embracing the cloud revolution
It’s anticipated that 85% of companies worldwide will adopt a cloud-first approach by 2025. As cloud adoption rises, securing these environments will become increasingly complex and critical.
Businesses using multi-cloud and hybrid-cloud strategies will require cloud-native defense solutions, which are security measures specifically designed to protect applications and data within cloud environments. This shift will drive demand for more advanced IAM (identity and access management) tools, encryption technologies, and data loss prevention strategies. Additionally, evolving data privacy regulations like GDPR (general data protection regulation) will further push organizations to strengthen their cloud security measures.

5. Strengthening cyber hygiene
Despite technological advancements, human error will remain a major cybersecurity vulnerability in 2025 and beyond. Phishing and other social engineering attacks are projected to remain a top cause of data breaches, with the average business facing more than 700 attempts each year. To combat this, companies must double down on employee training and awareness programs, fostering a culture of strong cyber hygiene.
Routine updates to cybersecurity policies, better password management, and regular simulated phishing tests will become standard practices. Additionally, fostering a proactive cyber safety mindset among staff will be as important as ever in safeguarding against human errors. This includes encouraging vigilance and reporting suspicious activities.
Emerging cybersecurity threats
With the cost of cybercrime expected to skyrocket to $13.82 trillion by 2028, staying ahead of emerging threats is paramount. Here are some of the most pressing challenges on the horizon:
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) rise
In 2023, over72% of businesses worldwide were impacted by ransomware. As theRaaS model gains traction on the dark web, ransomware kits will become increasingly accessible to non-technical criminals. This will lead to more frequent and severe attacks.
Deepfake fraud
Deepfakes are proliferating as they're used to impersonate executives, employees, and public figures. This technology will enable fraudulent activities like BEC (business email compromise) and the spread of misinformation, potentially manipulating markets and damaging organizations.
IoT vulnerabilities
As the number of interconnected IoT devices grows, new attack vectors emerge. Cybercriminals will exploit unpatched devices in smart homes, industrial environments, and critical infrastructure. Studies have found that over half of hospital IoT devices are vulnerable to attack. This not only poses significant security risks but potential legal penalties under regulations like GDPR and HIPAA (health insurance portability and accountability act).
5G network exploits
The rapid expansion of 5G — nearlytwo billion global connections in early 2024 alone — will introduce new defense challenges. The increased speed and connectivity provide more opportunities for attackers to exploit weaknesses in 5G-enabled devices and networks.
Autonomous systems hacks
“Cyber-physical” systems, which control physical processes through digital automation, are becoming prime targets. The size and complexity of autonomous systems in smart cities, factories, and grids offer large attack surfaces for hackers. A successful breach could lead to catastrophic accidents, city-wide shutdowns, or disruptions in essential sectors like manufacturing.
Related read:Are You Prepared for Today’s Modern Cyber Threats?
What will cybersecurity look like in 5 years?
In the next five years, the intersection of advanced technology and global collaboration will transform cybersecurity. Combining these two forces allows businesses to greatly improve its ability to defend against rising threats.
A shift from reactive to proactive strategies
A proactive approach will be at the forefront of this transformation. Organizations will rely on continuous monitoring systems to identify and address vulnerabilities in real time. Plus, AI-powered threat detection will play a key role in predicting and preventing attacks before they can cause harm. This shift from reactive to proactive strategies will dramatically reduce the window of opportunity for attackers and minimize the impact of breaches.
Improved data-sharing agreements and joint-security initiatives become vital
Additionally, as cybercrime continues to evolve on a global scale, international cooperation becomes crucial. Countries will need to work together to establish unified frameworks for addressing cross-border risks, enabling faster and more effective responses. Improved data-sharing agreements and joint security initiatives will be vital for countering the growing sophistication of organized cybercriminal networks.
The role of digital transformation in driving cybersecurity trends
While digital transformation drives innovation and efficiency for businesses, it also raises the need for strong cybersecurity to protect data, systems, and reputations. This is due to:
- Increased complexity: New technologies add layers to IT environments, making it harder to detect and fix protection gaps.
- Expanded attack surface: More devices and systems connecting to the internet mean more entry points for cyberattacks.
- New vulnerabilities: Emerging technologies create risks that traditional defense measures might not address, exposing businesses to new threats.
- Data privacy concerns: The reliance on personal data in digital spaces intensifies worries about privacy and security.
- Regulatory compliance: Stricter data protection laws force businesses to adopt strongcybersecurity practices to stay compliant.
Preparing for the future of cybersecurity, today
As we approach 2025, the cybersecurity landscape will continue to evolve at a rapid pace. AI-driven threat detection, zero trust architectures, and cloud-native security measures will be pivotal in shaping the future. Furthermore, the persistent risk of social engineering and human error underscores the importance of ongoing employee training and robust cyber hygiene.
To stay ahead, businesses must proactively update their defense strategies to prepare for future cybersecurity trends. Now is the time to assess vulnerabilities and implement measures to strengthen security. By staying informed and adaptable, organizations can safeguard their assets and ensure long-term resilience in the digital age.
Related Resources

Blog