Blog
Manufacturing supply chain 101: key concepts and FAQs

Every product goes through a supply chain. It’s a global network starting from the initial collection of raw materials all the way to distributors and wholesalers receiving final products. Valued at more than $23B in 2023, the global supply chain management market, including manufacturing supply chains, is expected to reach $63B by 2032.
Manufacturers play a critical role in both overseeing and optimizing the supply chain process. In this article, we provide a guide of frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to the management of the manufacturing supply chain.
What is manufacturing supply chain management?
Manufacturing supply chain management is the process of coordinating and optimizing the flow and production of goods, services, and information. In the manufacturing industry it:
- Ensures availability of materials and products
- Reduces costs
- Minimizes production or manufacturing delays
- Improves efficiency
Breakdowns at any point along the manufacturing supply chain can have a major effect on the future production and delivery of products. To effectively manage a supply chain, manufacturers must have the following components working in tandem:
Suppliers
Production cannot begin without the raw materials, components, or services needed. Suppliers are the ones who provide these materials, from metals and plastic to complex parts of specific machinery.
Procurement
To get the materials needed for production, manufacturers must source and purchase them from suppliers. This involves negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, and delivering what was ordered on time.
Manufacturing and production
Once materials are procured from suppliers, the manufacturing work begins, transforming these components into finished goods. Critical to this stage in the process are production planning and management, quality control, and equipment maintenance.
Inventory management
Throughout production, raw materials, in-progress work, and final or finished goods need to be properly monitored and controlled. Efficient inventory management helps prevent overproduction or overstocking of goods, keeping the production process running smoothly.
Warehousing
Materials, parts, and finished products should all be properly stored throughout the stages of prep, production, shipping, and distribution. Warehousing makes sure specific inventory is readily available whenever needed.
Logistics
Both materials and finished goods need to be transported and distributed between the points along the supply chain. All stages are included, starting with moving materials from suppliers to manufacturers and ending with final products reaching distributors.
Distribution
When ready, finished products are delivered to retailers or even directly to consumers, depending on how those items are sold. Successful distribution requires transportation-network management, order fulfillment needs, and even third-party logistics providers.
Demand forecasting
To support logistics and production processes, manufacturers must predict customer demand based on previous trends and the flow of a supply chain. Accurate forecasting can optimize inventory levels, reducing excess production or avoiding shortages.
Customer service
Maintaining customer satisfaction and trust along the manufacturing supply chain involves meeting — or exceeding — expectations at every point. This means sharing updates, providing timely delivery, quickly resolving issues, and producing quality products.
Does supply chain include manufacturing?
Manufacturing is an integral part of the supply chain, connecting suppliers to customers through the development of finished goods.
Within the supply chain components above, manufacturing falls between the procurement and distribution stages. It involves:
- Production planning: Makes decisions on what to produce and when, as well as how much to produce based on demand and availability of supply.
- Production process: Converts raw materials into finished products through assembly, fabrication, or processing.
- Quality control: Ensures products meet required standards before moving to the next stage of the supply chain.
How is supply chain function in a manufacturing environment different from other industries?
Supply chain function in a manufacturing environment is often more complex compared to other industries because of the varied logistics that are involved. For example, sourcing materials, planning production schedules, managing inventory, and maintaining quality control. In other industries, the focus may be more directional on things like digital assets or customer support.
A well-run manufacturing supply chain is one that is frictionless, minimizing potential workflow disruptions or setbacks. Technology and automation supports this by building more collaborative environments for manufacturing teams.
Schuster Concrete Companies needed to improve operational efficiency and employee productivity in order to keep its supply chain running smoothly. Implementing a central system to manage activities and updates from individual mobile devices across sites drastically increased site safety. Additionally, workflow automation allowed employees to better organize various business processes, no matter the level of complexity.
The supply chain in manufacturing environments has to drive value across all the components mentioned in this article. It’s a multi-faceted process that requires careful balance to succeed.

What is the role of a manufacturer in supply chain management?
Manufacturer's play a central role in supply chain management. They are responsible for taking raw materials and turning them into finished products. Manufacturers are also the primary link between suppliers and customers. Specifically, their role brings the following ten impacts.
- Driving the flow of goods all the way through the supply chain to distribution and sale
- Minimizing production delays and heavy costs via reliable supplier coordination
- Ensuring efficient production and prevention of bottlenecks with proper inventory management
- Maintaining quality control for product integrity, compliance, and customer satisfaction
- Fulfilling orders in a timely and cost effective manner to optimize resources
- Bringing products to market quickly and cost-effectively, maintaining efficient logistics and industry competitiveness
- Propelling product development and offering new or improved products to drive demand and strengthen the overall supply chain
- Reducing costs and enhancing reputation through sustainable manufacturing
- Using effective risk management to maintain supply chain continuity and minimize delays and financial losses
- Securing stronger relationships and repeat business due to customer satisfaction
Manufacturing companies increasingly need technology, specifically automation, to support positive relationships between manufacturers and suppliers. Automating workflows and time-consuming manual tasks increases collaboration for a more efficient supply chain.
What are the key challenges of managing the supply chain in the manufacturing industry?
There are key challenges manufacturers must address to stay competitive and keep supply chains cost effective. The following sections outline five critical ones to consider.
1. Disruptions to the supply chain
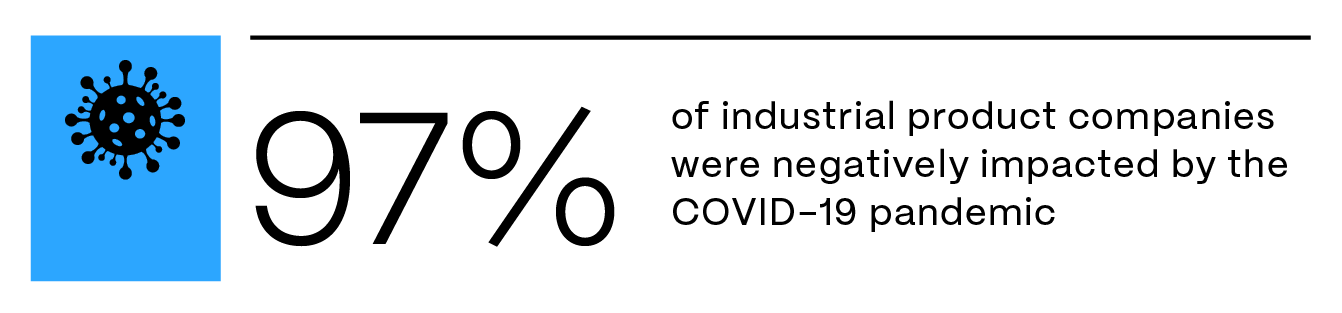
Unexpected events such as natural disasters or pandemics can cause production to completely stop. Stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic, nearly all (97%) industrial product companies were negatively impacted. This led to shipment delays, costly interruptions, and long-term supply shortages.
2. Difficulty forecasting demand and managing inventory
It’s a constant challenge to accurately predict consumer demand. Incorrect forecasts can cause overproduction, stockouts, and excess inventory. Efficiency and cost-effectiveness take a hit when this happens.
3. Inconsistent or unreliable suppliers
Sticking to production schedules is mission critical, and nothing throws off a timeline quite like an unreliable supplier. Supplier issues can compromise product quality, so strong supplier management is crucial.
4. Increasing costs for transportation and logistics
Rising transportation costs as well as mounting labor shortages and global distribution issues create major hurdles for logistics. As an example, average operational costs for trucking alone increased more than 23% in 2022.
Problems with technological integrations
While automation and technologies for data analytics are increasingly essential, integrating with legacy systems can be a challenge. Often requiring significant investment and tech expertise, integrations can be lengthy and difficult to adopt.
Maintaining regulatory compliance
Non-compliance with industry regulations and requirements for sustainability along the supply chain will result in fines. This also can lead to reputational damage and long-term financial risks or issues.
How can technology improve industrial manufacturing supply chain management?
Technology has a direct hand in making industrial manufacturing supply chain management more efficient, visible, accurate, and scalable. Here are six ways tech enhances supply chain operations.
- Automation and robotics in manufacturing facilities lead to faster production cycles and fewer manual errors.
- AI-powered data analytics make it easier to forecast demand, avoiding overproduction or stockouts.
- Real-time tracking through sensors provides a higher level of visibility for manufacturers to make more informed decisions.
- Cloud-based supply chain management platforms and tools improve collaboration between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.
- Blockchain technologies are increasingly used to secure transactions and shipments, maintaining regulatory compliance and trust.
- 3D printing gives manufacturers the ability to produce components or products on demand, reducing waste and improving responsiveness to new needs.
What are the benefits of optimizing manufacturing supply chain management?
Optimizing supply chains can bring the following benefits to manufacturers.
- Lower costs: Reduces operational costs such as transportation, inventory storage, and logistics.
- More efficiency: Reinforces communication and coordination for quicker production cycles and less lead time.
- Improved quality: Brings better material sourcing, higher quality standards, and production consistency.
- Higher profits: Boosts product quality leading to more customer loyalty and repeat business.
- Better risk mitigation: Identifies key risks like supply disruptions or compliance issues, making the supply chain more resilient and adaptable.
- Effective resource allocation: Uses materials and labor where it is needed most.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Elevates product quality and service leading to positive referrals.
- Increased sustainability: Lessens waste and overall carbon footprint.
Related read: Complete guide to manufacturing workflow management
Next Steps
Optimizing a manufacturing supply chain isn’t a box to check. It’s a strategic initiative that requires adept teams, advanced technology, and continual process improvement. How manufacturers manage and automate critical workflows across the supply chain matters.
The FAQs provided in this article can help you achieve a reliable and agile supply chain. See how automation can support manufacturers in getting more done.
Related Resources
